Dear Reader,
Welcome to yet another edition of The Agna Museletter.
So what fuels the incredible advances we see around us? Where do innovation and ingenuity come to life? What enables awe-inspiring structures and groundbreaking technologies?
ENGINEERING. Yes.
Let’s see how engineering got us here and where it’s leading us to.
Museletter Highlights:
- Agna Insights
Read through the transformative potential of Engineering in humanity’s endeavours - Agna Perspectives
Interesting and insightful reads we published over the last month -
Agna Team
Team Agna engagement highlights - On the ‘Front’ier Tech
Latest updates from the Frontier Tech Ecosystem - Agna Recommends
Team Agna’s curated recommendations for you
Agna Insights
Infrastructure, such as roads and bridges, underpins our daily lives, providing essential stability and order. These structures are more than just physical entities; they represent the foundation of human progress. Take, for instance, the ancient Roman aqueducts, which transformed urban living by efficiently delivering water, significantly improving public health and sanitation. Similarly, the Great Wall of China, built over centuries, exemplifies strategic ingenuity and the power of collective effort in ancient engineering. In modern times, engineering marvels such as the International Space Station (ISS) stand as a testament to cutting-edge technological progress, enabling sustained human presence in space and fostering international collaboration.

Mathematics and Geometry: The Blueprint of Engineering
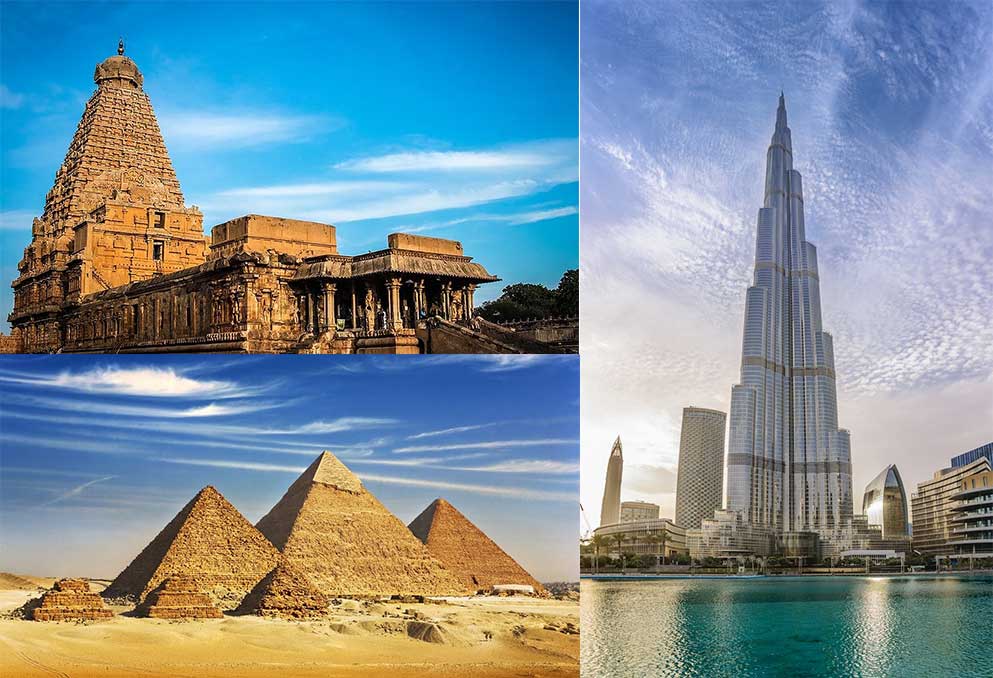
At the heart of these engineering marvels lie mathematics and geometry, which transform abstract ideas into tangible realities. These disciplines enable precise planning and construction, whether for a simple bridge, complex & intricate architectural temples, or a towering skyscraper. For instance, the use of calculus allows engineers to calculate load distributions and stress points in structures, ensuring they can withstand various forces. Geometry, on the other hand, guides the design of aesthetically pleasing yet structurally sound buildings, from the pyramids of Egypt to modern skyscrapers such as the Burj Khalifa.

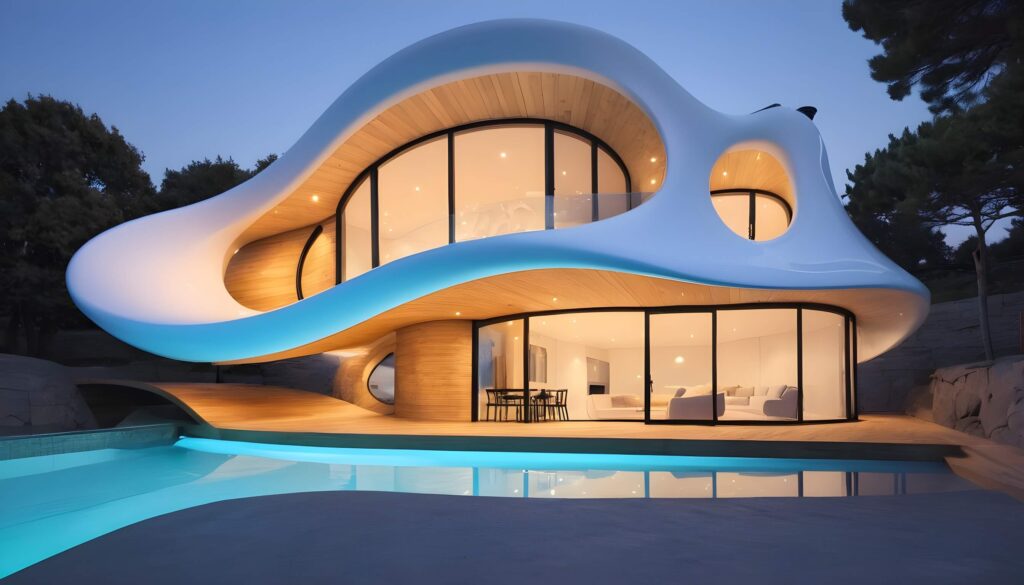
Technological advancements like 3D printing have further revolutionised the engineering landscape, most importantly finding applications in components used in space systems as well as the construction of buildings. This technology allows for rapid prototyping, enabling engineers to create detailed models of their designs before full-scale production. This accelerates the transition from concept to reality, reduces material waste, and allows for greater customisation with remarkable accuracy. One prominent example is the construction of The Wave House, (located in Heidelberg, Germany), spanning 6600 sq ft Europe’s largest that was brought to life ground up in just 140 hours!

Nature: The Eternal Engineer
Nature has long been a source of inspiration for innovative engineering solutions, a practice known as biomimicry. By studying and emulating the designs found in nature, engineers have developed groundbreaking technologies that solve complex human challenges. For example, researchers were inspired by the “common rose” butterfly to create a silicon film that mimics its wings. This innovation enhances solar cells, enabling them to capture more sunlight even in low-light conditions, thereby advancing sustainable energy use.

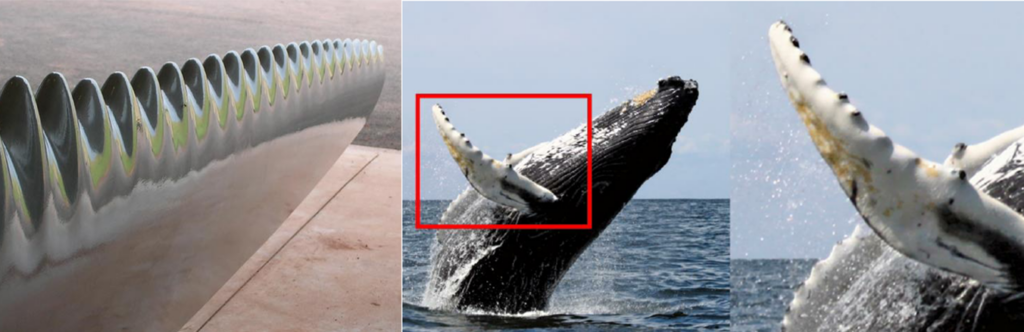
Similarly, the tubercles on humpback whale fins, which are small, rounded bumps, have guided engineers in improving designs for submarines, aircraft, and turbines. These tubercles disrupt water flow, reducing drag and increasing lift, which translates into improved efficiency and performance in human-made machines.
Engineering: The Driver of Technological Advancements
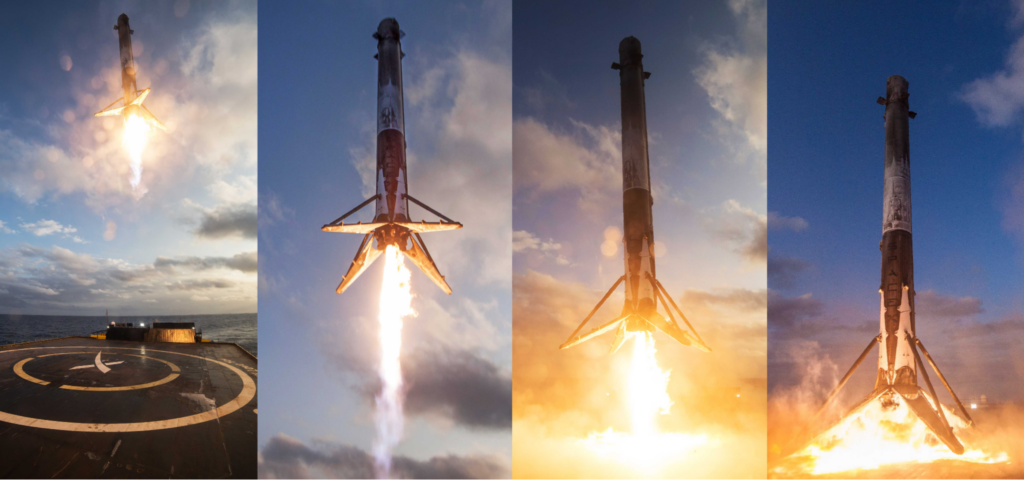
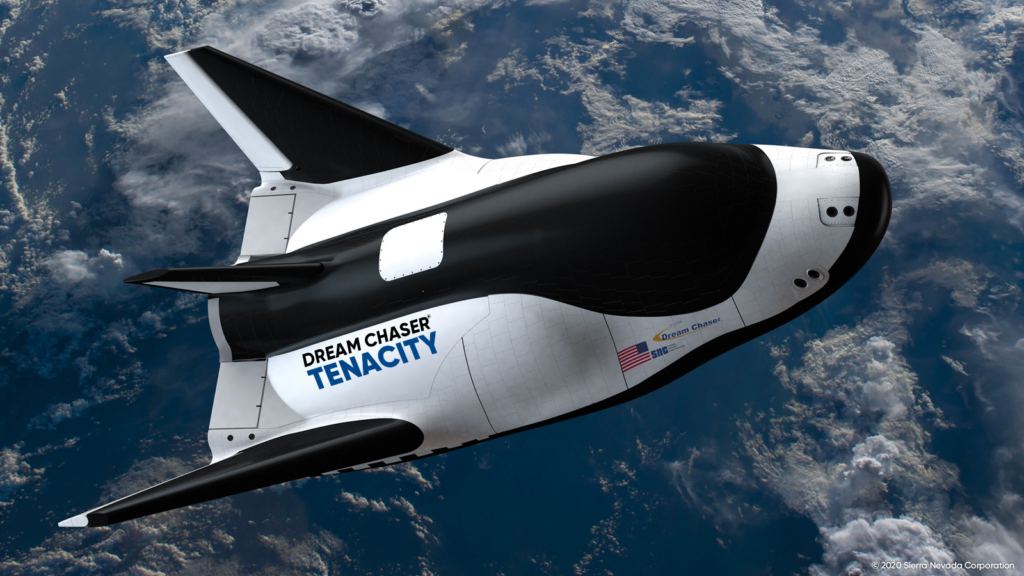
As engineers continue to draw inspiration from nature, they are also at the forefront of technological advancements that are reshaping our world. In the defence and aerospace sectors, private sector participation is proving to be a game-changer. For instance, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rockets have revolutionised space travel with their reusable design, significantly reducing the cost of access to space. Meanwhile, Sierra Space is making strides with their Dream Chaser spaceplane, which is designed to provide reliable cargo and crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. Additionally, their LIFE (Large Integrated Flexible Environment) habitat system is pushing the boundaries of human space habitation, potentially enabling long-duration missions to deep space. These innovations are not just advancing technology but also paving the way for humanity’s future in space.



Research and Development on emerging defence technologies such as hypersonic systems, which can travel at speeds exceeding five times the speed of sound, and advanced semiconductors, critical for sophisticated electronics, are setting new standards in defence capabilities. These innovations are not only boosting military effectiveness but are also creating new economic opportunities through dual-use technologies that serve both defence and civilian markets. For example, autonomous systems developed for military drones are now being adapted for commercial applications, such as delivery services and agriculture.
Engineering and Climate Change: A Sustainable Future
As we look toward the future, engineering’s role in combating climate change is becoming increasingly critical. Innovations in renewable energy systems, such as next-generation atomic and nuclear energy, are setting new benchmarks for clean power. The development of low-cost green hydrogen supply chains is another significant breakthrough, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Moreover, the electrification of heavy industrial processes and harnessing renewable energy sources like geothermal and tidal systems underscore engineering’s pivotal role in creating a sustainable energy future.
Carbon technology is also undergoing a revolution, with advances in low-cost CO2 capture systems, including Direct Air Capture (DAC), which are essential for reducing atmospheric carbon levels. Connected appliances for building energy control and sophisticated carbon accounting systems are making it easier to manage and mitigate carbon footprints effectively, facilitating the transition to a low-carbon economy.
The Future of Mobility: Engineering on the Move
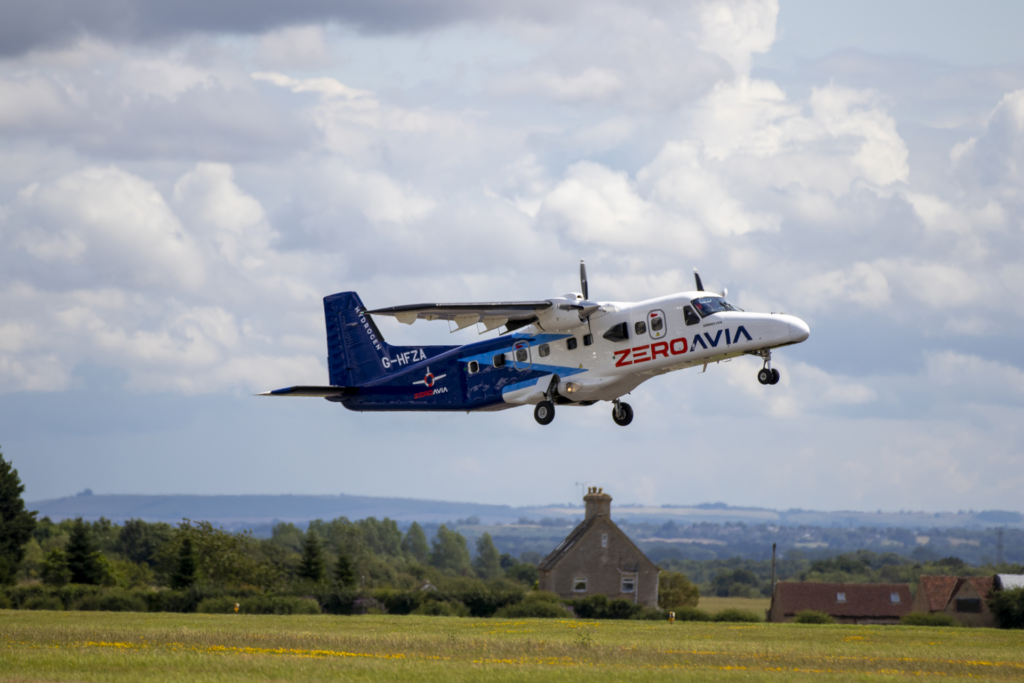
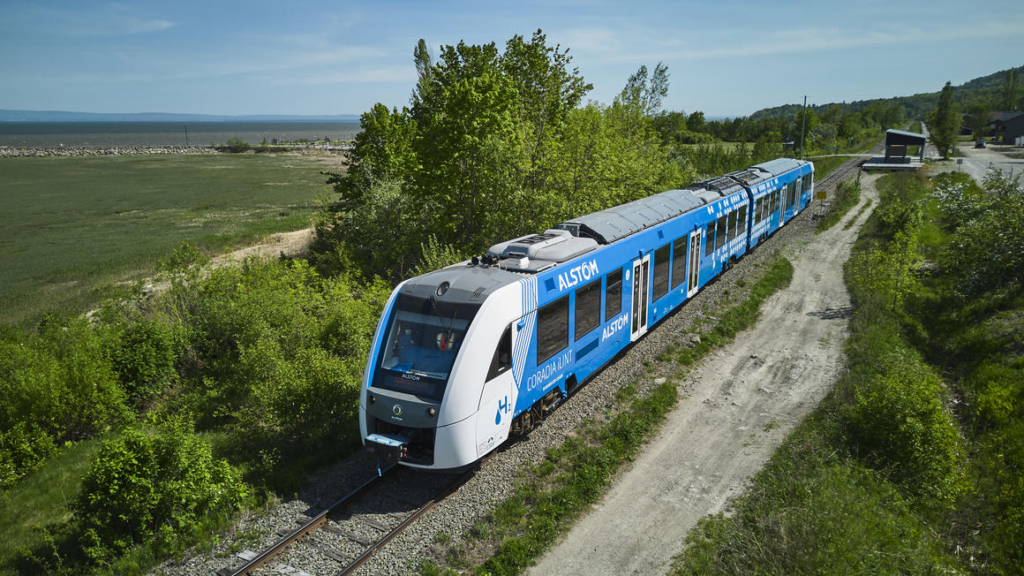
Groundbreaking innovations in electric and hybrid aircraft designs, advanced battery chemistries, and electric mobility infrastructure are reshaping the future of mobility. For example, ZeroAvia is pioneering hydrogen-electric aircraft, with successful test flights demonstrating the potential for zero-emission aviation. In the automotive sector, advances in solid-state batteries are extending the range and efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs), with companies like Toyota leading the charge. On the infrastructure front, cities like Oslo and Amsterdam are pioneering electric mobility with extensive charging networks, making EVs more accessible. Hydrogen mobility infrastructure is also advancing with examples like the Alstom Coradia iLint, the world’s first hydrogen-powered passenger train, which is already in service in Germany, offering a clean alternative to diesel trains. Meanwhile, algae-based biofuels are being explored as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, with companies like ExxonMobil working on scaling production for aviation and maritime industries. These engineering advancements not only reduce emissions but also pave the way for a greener and more sustainable transport sector, transforming how we move goods and people around the world.


Earth Observation and Space Technology: A New Frontier
Earth Observation (EO) is undergoing a significant transformation with advanced sensors like Synthetic Aperture Radars (SAR), infrared, and hyperspectral cameras, revolutionising data collection and analysis across the globe. SAR technology, used to monitor deforestation in the Amazon and floods in India, provides high-resolution images even in challenging conditions, aiding disaster management and environmental monitoring. Infrared cameras are crucial for wildfire detection, from California to Uttarakhand, India, enabling faster responses. Hyperspectral cameras are enhancing precision agriculture by monitoring crop health, as seen in global farms and UAE’s date palm plantations. These EO technologies also play a critical role in achieving net-zero emissions, with hyperspectral sensors tracking methane emissions worldwide, EO satellites monitoring urban air quality in India and conserving marine ecosystems in the UAE. By enabling precise monitoring of environmental changes and resource use, EO technologies are pivotal in the global fight against climate change and advancing sustainable development.
Satellite communications and connectivity are revolutionising everyday life by providing internet access to remote and underserved areas, and significantly enhancing healthcare through telemedicine. For example, SpaceX’s Starlink project has brought high-speed internet to isolated regions in Alaska, enabling residents to access online education, e-commerce, and emergency services that were previously out of reach. In healthcare, satellite connectivity is making a profound impact through telemedicine. In rural India, for instance, doctors use satellite-enabled teleconsultation platforms to diagnose and treat patients in remote villages, where specialist care was once unavailable. These advancements are not just technological marvels; they are lifelines for millions of people, bridging the gap between urban and rural areas, and ensuring equitable access to essential services across the globe.
In conclusion, the role of engineering in shaping our world extends far beyond the physical structures we see around us. From the ancient marvels that laid the foundation for civilizations to the cutting-edge technologies propelling us into the future, engineering continues to be the driving force behind human progress. As we embrace the opportunities of the 21st century—climate change, space exploration, and sustainable development—engineering will remain at the forefront, guiding us toward innovative solutions that balance the demands of growth with the imperatives of sustainability. The future, much like the past, will be built on the ingenuity, creativity, and resilience of engineers who dare to dream and shape a better world for all.
Agna Perspective
Engineering is certainly about meticulous planning and precise calculations. But sometimes, the most transformative discoveries are stumbled upon by chance, a twist of fate that rewrites history. Read here
Culture has always influenced engineering, blending ancient wisdom with modern tech. From Egypt’s pyramids to today’s earthquake-resistant buildings, history showcases our creativity and innovation. Read here
How from the wheel to #RenewableEnergy technologies, each eureka moment has significantly impacted society and paved the way for future advancements. Read here
Team Engagement:

Meta Decrypt meet-up
Our Founder- Pranav Sharma- attended the Bitcoin Meetup as one of the panellists, organised by Meta Decrypt at Yas Creative Hub, Abu Dhabi, exploring Real World Asset Tokenization in the luxury space.
On the ‘Front’ier Tech:
- The SETI Institute’s study using the Murchison Widefield Array marks a groundbreaking search for alien technology in galaxies beyond our own, focusing on low radio frequencies.
Read Here - Indian aerospace startup Space Zone India is set to launch the country’s first reusable rocket, Rhumi-1, on August 24, aiming to revolutionise space travel with cost-effective, hybrid propulsion technology.
Read Here - Adani Power has incorporated a wholly-owned subsidiary, Adani Power Middle East Ltd., in Abu Dhabi to invest in power, infrastructure, and related fields. Read Here
Agna Recommends:
- The Being An Engineer podcast is a central repository through which they collect and share industry knowledge & best practices associated with the discipline of engineering. Listen
- The Pragmatic Programmer by Andy Hunt and Dave Thomas A surprisingly untechnical book that includes dozens of real-world applications for non-engineers.
- Skin in the Game: The Hidden Asymmetries in Daily Life This book explores how having personal stakes in decisions—whether in business, politics, or life—creates hidden asymmetries that drive true accountability and risk management.
Questions? Feedback? Different perspective?
We invite you to engage with us and collaborate.
Warm Regards,
Team Agna
Click below to join our mailing list for The Agna Museletter.